The Axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum), a fascinating aquatic creature, is often hailed as nature’s “healing machine” due to its remarkable regenerative abilities. This unique species, native to lakes near Mexico City, is not only a subject of intense scientific study but also a species on the brink of extinction. The Axolotl’s ability to regenerate lost limbs, organs, and even parts of its heart and brain is unmatched in the animal kingdom, earning it comparisons to fictional characters like Wolverine, whose healing powers are legendary.

A Marvel of Regeneration
What sets the Axolotl apart is its ability to heal injuries and regenerate tissues that would be impossible for most other creatures. When an Axolotl loses a limb or suffers damage to vital organs, it can regenerate the tissue, regrowing it completely without scars. The process begins when the injury occurs, triggering a complex biological response. Within hours, the wound is covered with a layer of cells, preventing infection and blood loss.
The Regeneration Process
The true magic happens over the next few days: blastema cells — which are specialized stem cells — begin to form at the site of the injury. These cells are able to differentiate into various tissue types such as muscle, bone, nerve, and even blood vessels. Over the course of 30 to 60 days, the damaged body part is regrown to its full functional state, restored as if nothing had ever happened.
This regeneration process has been studied intensely by scientists worldwide, with particular interest in understanding how these cells can function in such a precise and organized manner. Dr. James Goodwin from the MDI Biological Laboratory in Maine has stated, “The ability of Axolotls to regenerate organs, limbs, and even parts of the heart and brain is one of nature’s greatest mysteries, and we’re hopeful that understanding this could lead to breakthroughs in human medicine.”
The Secret to Their Immunity and Cancer Resistance
Not only can Axolotls regenerate lost body parts, but they also possess extraordinary resistance to cancer. Research has shown that these creatures are up to 1,000 times more resistant to cancer compared to typical mammals. Their immune system, particularly the role of macrophages (a type of white blood cell), plays a crucial part in both the regeneration process and their cancer resistance.
Macrophages in Axolotls don’t just protect against infection; they actively assist in healing and tissue regeneration by repairing nerve cells and regenerating damaged organs. This sets them apart from human macrophages, which focus primarily on detecting and destroying harmful pathogens. This discovery has made Axolotls a focal point of research into cancer and regenerative medicine, with the hope that we can someday apply similar regenerative techniques to human health.
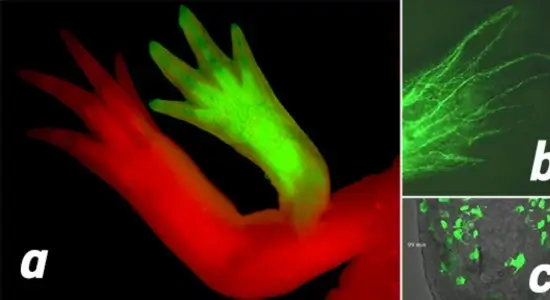
a – Scientists Successfully Grew a “Third Arm” on an Axolotl
In a groundbreaking experiment, researchers managed to stimulate the growth of an extra limb—essentially a third arm—by using targeted regenerative proteins.
b – Axolotl Cells Can Remember the Original Shape and Scars of Lost Limbs
Studies show that axolotl stem cells “remember” the exact size, shape—even tiny scars—of the missing limb during regeneration.
c – Zoomed-In Images Reveal White Blood Cells Actively Repairing Damaged Tissue
High-resolution imaging captured white blood cells busily repairing nerves and tissue—unlike human cells, which primarily focus on defending against pathogens.
Axolotls and Their Role in Science
The Axolotl is not just a biological marvel; it is also a living lab for scientists. The creature’s ability to regenerate complex organs, such as the heart, spinal cord, and even the brain, offers researchers a rare opportunity to study biological processes that were previously thought impossible.

Many researchers are focused on the genetic mechanisms that allow Axolotls to regenerate. The Axolotl genome, which was sequenced in recent years, has provided vital insights into how this process works at the molecular level. Understanding the genetic code behind the Axolotl’s regenerative powers could one day unlock the potential to develop therapies for humans suffering from injuries or conditions that currently have no cure, such as spinal cord injuries or severe burns.
The Struggle for Survival
Despite their fascinating abilities, Axolotls are currently listed as critically endangered in the wild. Due to habitat destruction, pollution, and invasive species, their population has dramatically declined in their native lakes. Conservation efforts are underway, but the future of the Axolotl remains uncertain. Its survival is now largely dependent on breeding programs and its popularity in research.
Efforts to preserve the Axolotl are crucial, as its ability to regenerate could hold the key to advancements in medicine that benefit all of humanity. With continued study, scientists hope to unlock even more secrets from this extraordinary creature.
Key Takeaways
-
Regenerative Powers: Axolotls can regenerate lost limbs, organs, and even parts of the brain.
-
Healing Process: The regeneration process involves blastema cells, which can differentiate into various tissue types.
-
Cancer Resistance: Axolotls are 1,000 times more resistant to cancer than most mammals.
-
Scientific Research: The Axolotl is a key species in regenerative medicine, offering potential insights into human healing and cancer treatment.
Did you know there are many other intriguing phenomena in the animal world? Explore more about Natural Regeneration in animals like the axolotl and other remarkable biological secrets that scientists are still uncovering.