THIS IS THE ONLY KNOWN ANKYLOSAUR HATCHLING FOSSIL IN THE WORLD
It’s hard to imagine something as terrifyingly armored as an Ankylosaur starting out small. These Cretaceous tanks were the dinosaurs with built-in defense systems: bony plates covering their backs and a massive, bone-crushing club on their tail. But before they became prehistoric panzers, they were just—well, eggs.
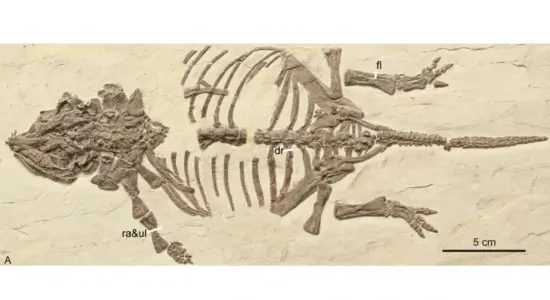
That’s why the discovery of “Tiny,” the only known Ankylosaur Hatchling Fossil in the world, is such a massive deal in paleontology. This specimen gives scientists a rare, crucial glimpse into the growth and development of the most heavily armored dinosaurs to ever walk the Earth.
Meet Tiny: The Ultimate Defense Baby
The fossil, affectionately nicknamed Tiny by the research team, was discovered in Alberta, Canada. It belongs to the Euoplocephalus tutus species, one of the most famous types of Ankylosaur. But what makes this find truly spectacular is its size—or lack thereof.
Tiny is a partial skeleton, including skull and armor elements, and it is estimated to have been only about 1 to 1.5 meters (3.3 to 5 feet) long when it died. Considering an adult Euoplocephalus could stretch up to 6 meters (20 feet) long and weigh over 2 metric tons, Tiny was, fittingly, incredibly tiny.
The preservation of this specimen is exceptionally rare because baby dinosaurs, especially hatchlings, have delicate, porous bones that rarely survive the fossilization process. Finding a baby Ankylosaur is exponentially more difficult, given the odds.
The Mysteries of Dinosaur Armor
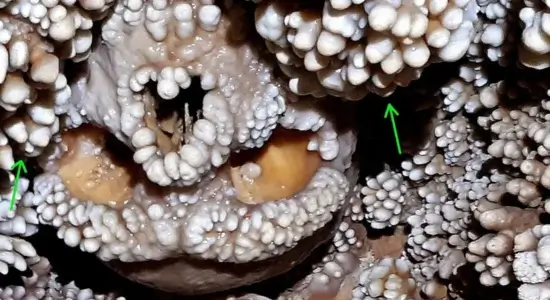
The most fascinating aspect of Tiny’s fossil is its armor, which looks structurally different from that of an adult. Adult Ankylosaurs sported thick, fused bony plates called osteoderms (which are basically skin-level bones), often topped with spikes. These plates were integrated into their skin, forming a solid shield.

In Tiny, however, the armor pieces were still small, scattered, and notably unfused. This is critical. It suggests that the sophisticated, interconnected armor system that defined the adult Ankylosaur only developed later in life. This is evidence that the babies likely didn’t rely on the heavy, fused armor for protection, possibly using camouflage or parental defense instead.
The study confirms that these armored plates grew and strengthened rapidly during the dinosaur’s adolescence, essentially adding layers of defense as the animal grew in size and became a more tempting target for predators like the T. Rex.
Insights Into a Slow Life
Beyond the armor, Tiny’s fossil helps scientists understand the growth rates of these colossal animals. Studies of its bone structure suggest that Euoplocephalus had a relatively slow, sustained growth rate compared to some faster-growing theropods (like the velociraptor).
This slow growth aligns with the theory that animals with heavy body armor and complex defensive structures invested energy into building those protective features rather than maximizing speed or rapid development. Tiny’s remains confirm that the evolution of body armor came with a trade-off: a longer, more vulnerable childhood. This single, small fossil is a huge piece of the puzzle, revealing not just what they looked like, but how they lived.
The process of finding, studying, and preserving fossils like Tiny is a painstaking effort that connects us directly to deep time. Yet, the story of the ancient world isn’t limited to just bones. Sometimes, what we find reveals a surprising connection to other prehistoric life. For instance, while paleontologists focus on how the Ankylosaur grew its massive armor, archaeologists were recently stunned by the discovery of an ancient Mammoth Ivory Boomerang. This incredible tool, carved by ancient humans thousands of years later, reminds us that the giants of the past—from the armored dinosaurs to the woolly mammoths—continue to shape the stories we uncover today.
🧠 Did You Know?
The search for rare dinosaur fossils continues to rewrite history, especially concerning how these giants emerged from their eggs!
-
The First Eggs: Before the discovery of the first Ankylosaur Hatchling Fossil, one of the most famous early finds was the discovery of Oviraptor eggs in Mongolia in the 1920s. Scientists mistakenly thought the Oviraptor (Egg Thief) was stealing eggs, but it was later revealed the dinosaur was actually tending to its own nest.
-
T. Rex Toddlers: The Ankylosaur wasn’t the only giant with a vulnerable infancy. While we still debate the full appearance of baby T. Rex, evidence suggests that the massive predator was born with delicate features and likely required years to develop its crushing jaw power. Like Tiny, these young predators had to survive a long period before reaching their terrifying adult form.
ref : iflscience , ScienceAlert